In the push toward energy efficiency, water source, heat pump systems should be considered as energy can be transferred from zone-to-zone to be reused instead of expending new energy to heat or cool the zone. This form of energy recovery is highly efficient and also provides the ability to independently control each zone based on heating or cooling demand. Each zone consists of a heat pump, which is a self-contained heating and cooling unit, that utilizes the vapor compression cycle with a refrigerant-to-air heat exchanger and a refrigerant-to-water heat exchanger. This creates two heat exchange coils that operate as either the condenser or evaporator, and each coil is dependent upon the heat-pump mode of operation.
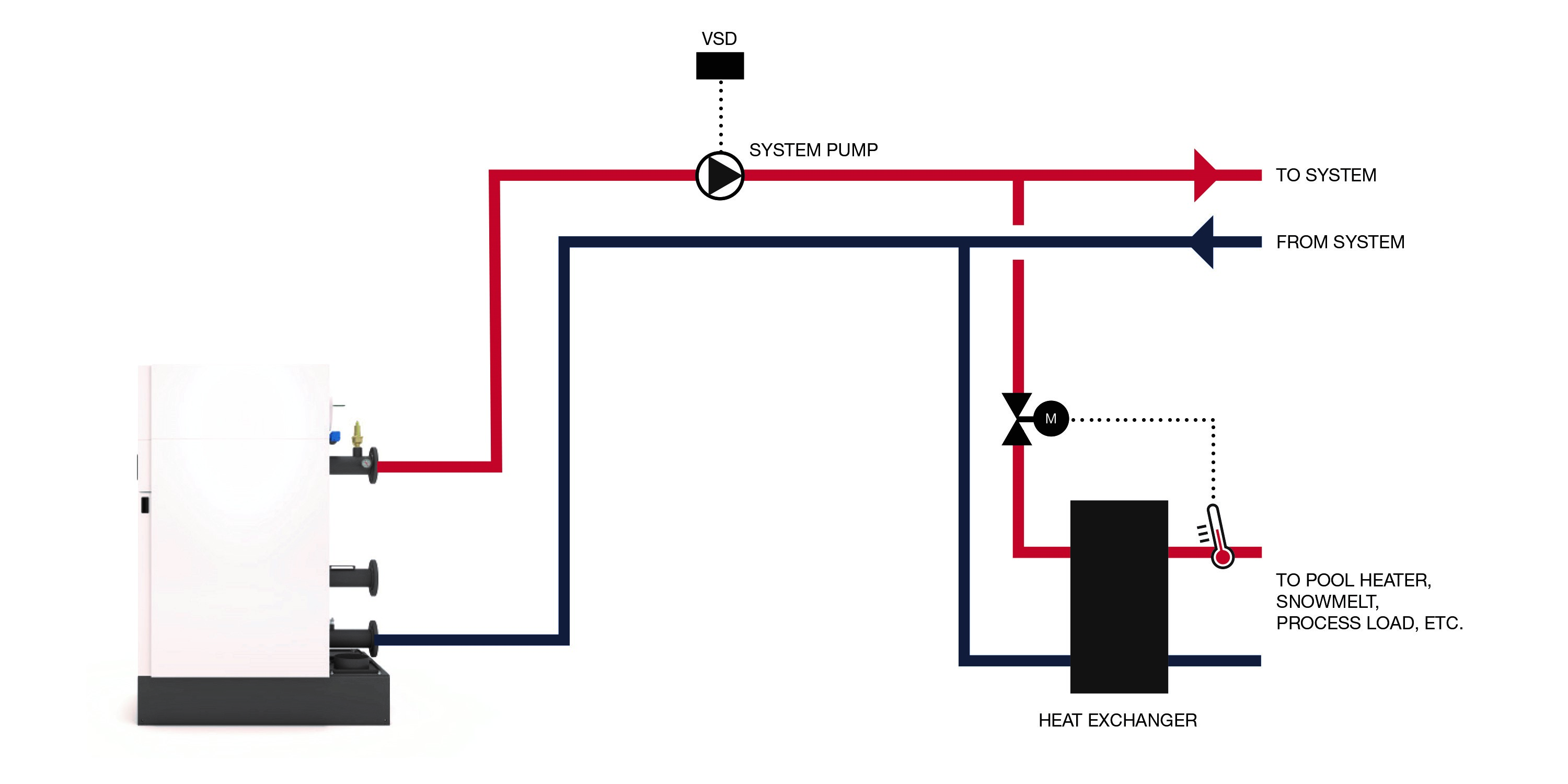
A hybrid system is a system that consists of both condensing and non-condensing boilers in the same system. Due to the more robust construction of a condensing boiler as well as the materials necessary to protect it from the acidic condensate, a condensing boiler is more expensive compared to a similar-sized non-condensing boiler. If the cost for a fully condensing boiler plant exceeds the budget, the best approach is a hybrid system that can use the advantages of each system to its benefi t based on the hot water return temperature. Hybrid applications also work well in retrofit applications, where a legacy, non-condensing boiler is maintained for design-load days, while a more efficient condensing boiler is utilized whenever possible.
Heat recovery chiller systems, or high lift chiller applications, also can be used with condensing boilers as the systems complement one another, similar to a hybrid system. In this application, the intent of the heat recovery chiller is to provide hot water at a temperature high enough to heat the building, whereas a condensing boiler requires a low hot water return temperature to promote condensing. Utilizing both systems provides redundancy in operation when there is not the ability to run the heat recovery chiller, which requires a constant cooling load to function properly. This configuration also provides fuel flexibility, enabling the system to operate with either the heat recovery chiller or condensing boiler based on fuel price for the lowest operating cost.